🐳 Introduction to Docker
Docker is an open container management platform. It’s a software platform used to run applications inside isolated environments called containers.
By using Docker, you can separate your application from the infrastructure, making it easier to build, ship, and run applications efficiently. It helps developers and DevOps engineers deliver software faster and more reliably across different environments.
With Docker:
- You manage infrastructure the same way as applications.
- You can build, test, and deploy faster.
- The gap between writing code and running it in production is significantly reduced.
🖥️ Virtual Machines vs Containers
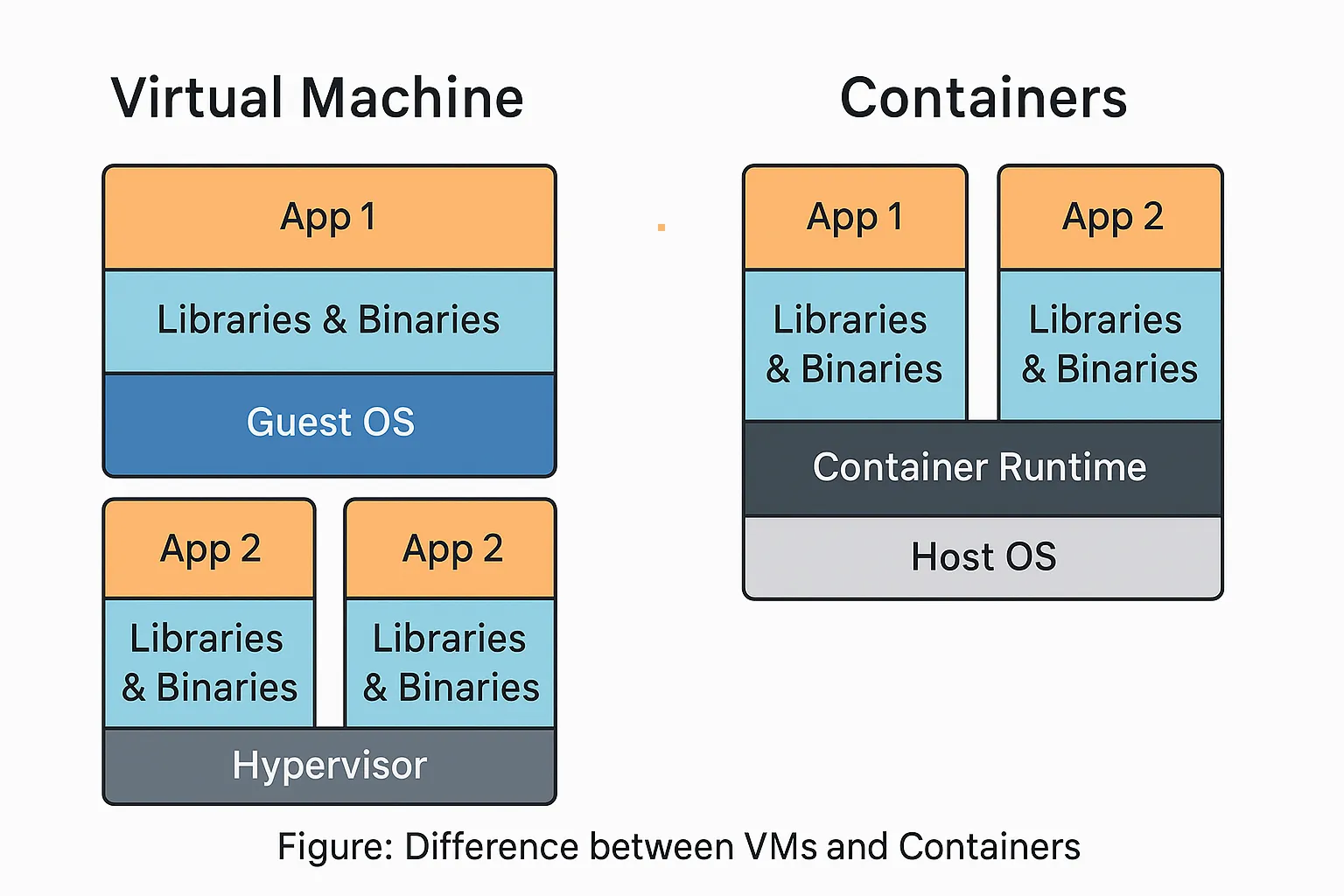 Figure: Difference between VMs and Containers
Figure: Difference between VMs and Containers
🔹 Virtual Machine (VM)
A Virtual Machine is a complete operating system that runs on virtualized hardware. It relies on a hypervisor to simulate hardware and allow multiple VMs to run on the same physical machine.
Each VM includes:
- A full guest operating system
- Virtual hardware (CPU, memory, disk)
- An app and its dependencies
🔻 Downsides:
- Heavy (GBs in size)
- Slower startup
- More resource consumption
🔹 Containers
Containers, on the other hand, share the host system’s OS kernel but run isolated processes for different apps. They are lightweight, fast, and ideal for microservices and CI/CD.
Each container includes:
- The application
- All its dependencies
- Shared OS kernel (but isolated runtime)
✅ Benefits:
- Much smaller in size (MBs)
- Start instantly
- Multiple containers can run on a single host
- Less overhead compared to VMs
⚙️ Docker Architecture
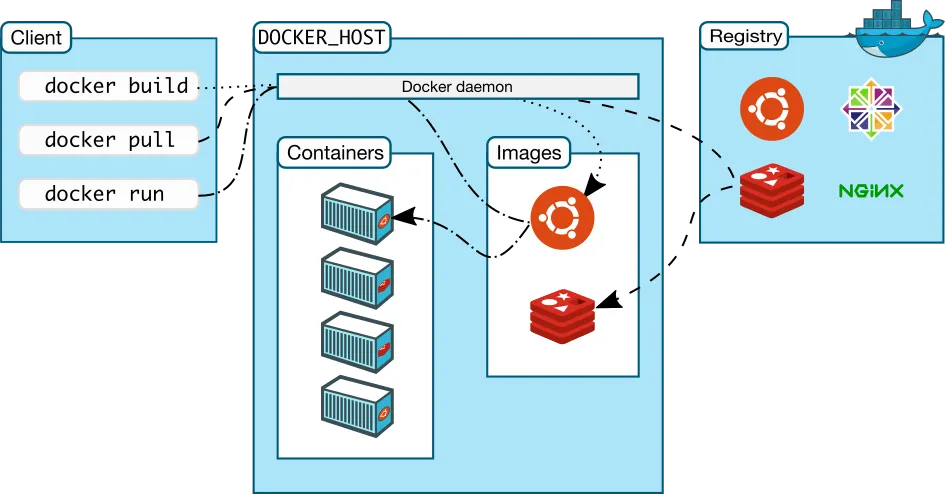 Figure: Docker’s Client-Server Architecture
Figure: Docker’s Client-Server Architecture
Docker follows a client-server architecture with the following components:
- Docker Client: The user interface that sends commands (like
docker run) to the Docker daemon. - Docker Daemon (dockerd): The background service that manages containers, images, networks, and volumes.
- Docker REST API: Communication bridge between the client and the daemon.
- Docker Images: Read-only templates used to create containers.
- Docker Containers: The actual running instances of images.
📡 Communication happens via:
- UNIX sockets (on Linux/macOS)
- Network interfaces (for remote connections)
🔚 Conclusion
Docker makes modern application development more efficient by providing a clean, isolated environment for apps. It replaces bulky VMs with fast, lightweight containers — making your infrastructure leaner and your deployment cycles shorter.
In future posts, we’ll cover how to install Docker, write Dockerfiles, and create real-world containerized apps. Stay tuned!
~ Rao Shahzaib